SPECIAL TYPE OF FEVER
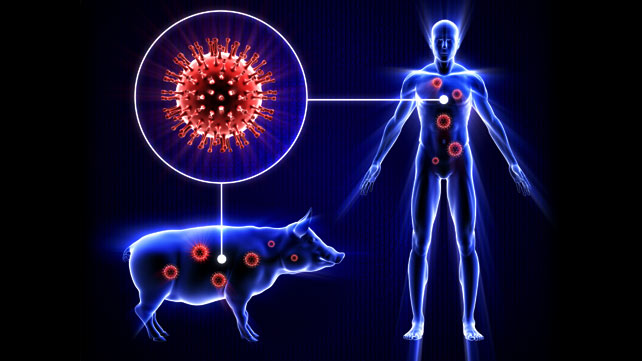
Human swine flu is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by a new strain of influenza virus. Symptoms of human swine flu include a fever (temperature over 38°C), cough, sore throat, aches and tiredness. Human swine flu is also known as human swine influenza, influenza A (H1N1) virus or H1N1 influenza 09.

Viral fever is an acute viral infection. The most common viral fever is the seasonal flu or influenza. Children can catch viral fever easily.
Chikungunya (chik-un-GUN-yuh) is a virus transmitted by mosquitoes that causes the sudden onset of fever and severe joint pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fatigue, muscle pain, headache and rash. Signs and symptoms of chikungunya usually appear two to seven days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
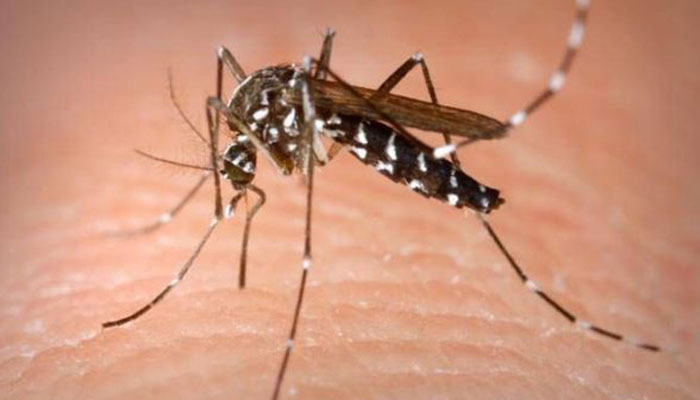

Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. This may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash.
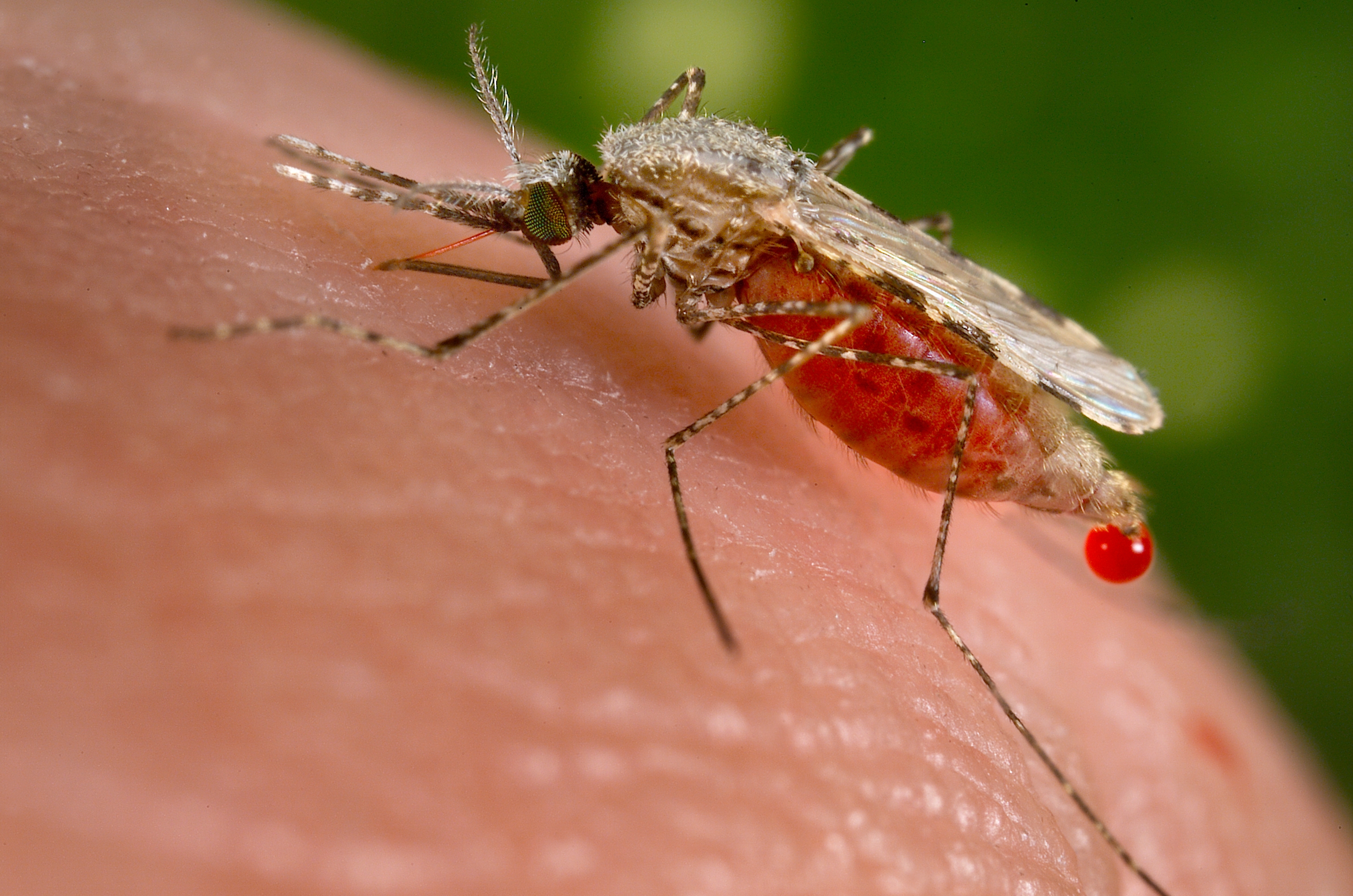
Malaria is a febrile illness characterised by fever and related symptoms. However it is very important to remember that malaria is not a simple disease of fever, chills and rigors. In fact, in a malarious area, it can present with such varied and dramatic manifestations that malaria may have to be considered as a differential diagnosis for almost all the clinical problems! Malaria is a great imitator and trickster, particularly in areas where it is endemic.


Bird flu, or avian flu, is an infectious viral illness that affects mainly birds.
Most bird flu viruses dont affect humans, but some strains — particularly H5N1 and H7N9 — can in rare cases cause serious infections in people.
Bird flu is transmitted to humans through direct or indirect exposure to live or dead birds infected with the virus, such as by working with poultry (farming) or consuming raw or undercooked meat, blood, or eggs.
Your Reaction?